Recarburizer for synthetic cast iron application case
1. Overview of synthetic cast iron
Due to the fierce competition in the casting Market and the higher and higher requirements for casting quality, but the lower the price, and the more stringent environmental protection requirements, many local governments have banned the use of cupola to melt molten iron. In terms of the price of raw materials, due to the large amount of precipitation and retention of scrap steel in the society, and the price of scrap steel is much lower than that of new pig iron, the method of scrap steel plus recarburizer has been widely used to produce cast iron, namely "synthetic cast iron". In the production process, if the process operation is correct, not only the chemical composition and temperature of cast iron are easy to control, but also the comprehensive physical properties of castings can be improved, but also the production cost of castings can be reduced. In the process of continuous development and improvement of synthetic cast iron technology, the amount of scrap steel is also increasing, from about 40% at first to 80% now. Electric furnace smelting cast iron does not have recarburizer source like cupola. In order to obtain qualified carbon content, adding
recarburizer is an essential measure. The selection and application method of recarburizer will improve the structure of cast iron, It is very important to improve the comprehensive physical properties of cast iron.
2. Types of commonly used
recarburizer
There are many types of
recarburizers, and there are many materials that can be used as cast iron
recarburizer. The production process of recarburizer is also different. There is a big difference in quality and a big price difference. The correct choice of recarburizer is required for the geometric shape and quality requirements.
High-quality
recarburizer is generally graphite petroleum coke(GPC), that is, under high temperature conditions, the arrangement of carbon atoms is in the microscopic form of graphite, as shown in the attached drawings.
Graphite recarburizer
According to the usage of most factories, combined with the author's experience of using recarburizers in the production process, only two commonly used recarburizers are briefly introduced.
1. Artificial graphite
Among the commonly used recarburizers, artificial graphite is the best quality recarburizer.
The main raw material for the manufacture of artificial graphite is powdered high-quality calcined petroleum coke, in which a small amount of other auxiliary materials are added. After the raw materials are prepared, they are pressed into shape, and then processed in a non-oxidizing atmosphere at 2500~3000℃ to make them graphitized. After high temperature treatment, the ash, sulfur, and gas content are greatly reduced. Because of its many production processes and long production cycle, the price is higher.
The artificial graphite recarburizers commonly used in foundries are mostly recycled materials such as chips in the manufacture of graphite electrodes, waste electrodes and graphite blocks.
2. Calcined petroleum coke
Calcined petroleum coke is currently a widely used
recarburizer.
Petroleum coke is a by-product of refining crude oil. Crude oil residues and petroleum pitch obtained by atmospheric distillation or vacuum distillation can be used as raw materials for manufacturing petroleum coke, and after coking, raw petroleum coke can be obtained. Raw petroleum coke has a high impurity content and cannot be used directly as a
recarburizer. It must be calcined first. The
calcined petroleum coke is to remove sulfur, moisture and volatiles. Calcining raw petroleum coke at 1200~1350°C can make it into basically pure carbon. The ingredients of various petroleum coke products are listed in Table 1 (for reference).
Table1 Petcoke products content
|
Name |
Fixed carbon value% |
Sulfur% |
Ash% |
Volatile% |
Moisture% |
|
CPC |
98.5 |
0.02-3 |
0.2-0.5 |
0.3-0.5 |
≤0.5 |
|
GPC |
99 |
0.01-0.03 |
0.1-0.5 |
|
≤0.5 |
|
Graphite powder |
99.9 |
0.01-0.03 |
0.01-0.03 |
|
≤0.2 |
①
Calcined petroleum coke , because it has not been calcined at high temperature, or the calcining temperature is low and the time is short, the nitrogen content is generally about 9000ppm (1ppm=10-6), and the sulfur content is also high, which cannot be used on white paper. Draw clear traces. ②High-temperature
graphitized petroleum coke:GPC, the nitrogen content is 300-500ppm, and the sulfur is much lower than the former. Clear marks can be left on white paper. ③The best quality high-temperature:Graphite powder, with a nitrogen content of 100ppm. Sulfur is lower than the former. It can leave clear marks on white paper, and feel comfortable, just like a 6B pencil.
According to the Baiyuncarbon’s experience from several factories, many companies often pay attention to the price of the recarburizer and the fixed carbon, sulfur, ash, volatile matter, and moisture content in the recarburizer when purchasing recarburizers. These are of course important for stabilizing product quality and reducing production costs, but an important parameter is often overlooked, that is, the "nitrogen" content in the recarburizer.
The role of nitrogen in cast iron has two sides: According to the information, the strength of gray cast iron can be increased by 5 to 7 MPa for every 10 ppm increase in nitrogen content, and the hardness can be increased by 3 to 4 HBW. It is generally believed that when the nitrogen content is 70-120ppm, the graphite can be shortened and the tail can be passivated. Nitrogen can strengthen the pearlite matrix and improve the mechanical properties of cast iron. However, when the nitrogen content of cast iron exceeds the critical point (generally considered to be about 140ppm), it will cause nitrogen holes in the casting.
In recent years, although many foreign companies, especially in Japan, require the nitrogen content of cast iron to be 60-120ppm and the titanium content to be less than 0.025%. However, nitrogen is an inert gas after all.
Generally, nitrogen exists in cast iron in three forms: one is dissolved in liquid or solid cast iron; the other is to form nitrides with elements in molten iron; the third is to precipitate from molten iron and exist in the form of elemental gas to form pores . According to some information: when the use amount of scrap in the charge is 15%, the nitrogen content in cast iron is about 0.003% to 0.005%; when the use amount of scrap in the charge is 50%, the nitrogen content in cast iron is about 0.008% to 0.012 %; When the charge is all scrap steel, the nitrogen content may be as high as 0.014% or more. Due to the increasing amount of scrap steel added and the amount of recarburizer added, attention must be paid to the nitrogen content in the recarburizer. In order to avoid porosity defects in castings, when purchasing recarburizers, you must choose products with low nitrogen content. If possible, check the nitrogen content in recarburizers. Now, let alone the nitrogen content in the
recarburizer, it is the nitrogen content in the cast iron, and many companies cannot accurately analyze it. According to the author’s experience, when buying recarburizers, you should buy products from large enterprises. You can check with the manufacturer before buying and go to users who have already used it. Once the quality of the castings is stable after use, don’t take it lightly. If you change customers, even if you are a fixed customer, you must try out a few furnaces first when you buy in batches again, and then use them in batches when you are sure that it will not affect the quality of the castings.
3. Case study
(1) Case 1 Our company and a large casting company in Zhumadian have been using the
recarburizer produced by a company in Wugang group for a long time, and the product quality is very stable. Afterwards, the recarburizer produced by a SD company is used intermittently. Porosity appears in the batch, and in severe cases, it can be found after the casting falls out of sand. Metallographic analysis: There is no graphite around the pores, and the edges are white and bright, showing a "carbon-poor" phenomenon. Compared with the gold image map provided by "Elkem International Trade (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.", it should belong to the nitrogen hole. Table 2 shows the test results of chemical composition of the furnaces with pores.
Table 2 Chemical composition of stomata furnace (mass fraction)%
|
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
Cu |
Gr |
Sn |
N(ppm) |
|
3.41 |
1.81 |
0.78 |
0.04 |
0.085 |
0.5 |
0.44 |
0.048 |
|
Note:Nitrogen content uses the Nitrogen Oxygen Hydrogen Tester produced by American Leco Company, model TCH-600
(2) Case 2 A factory in Mengcun County, Cangzhou, Hebei, produces construction fasteners. The material selected is QT450-10. The wC of ductile iron is controlled at 3.5%~3.7%, and the CE is controlled at 4.5%~4.6%. The ingredients and test results are shown in Table 3.。

According to Table 2, calculate the absorption rate of the recarburizer:
Excluding burning loss, recarburizer should be substituted for carbon amount=95%×3.8%=3.61%
Excluding burning loss, all charge should be substituted for carbon amount = 3.61% + 0.7% + 0.225% = 4.535%
The actual substitution of carbon into the recarburizer=3.3%-0.7%-0.225%=2.375%
Absorption rate of recarburizer={1-[3.61(%)-2.375(%)]÷3.61(%)}×100%≈66%
It should be noted that the absorption rate of this kind of coal-based recarburizer is not only low, but also when the charge is melted and the furnace mouth slag is cleaned, if the power is cut off or the power is reduced for some reason, it is hung on the furnace wall without melting. The recarburizer will float and fill the liquid surface; in addition, not only are there pores on the casting, even the running iron that falls on the sand box during pouring is about 5mm thick, and there will be several small pores on the fracture.
After replacing with graphite recarburizer, the absorption rate of recarburizer is about 85%, which not only reduces the amount of recarburizer added, but also eliminates the above-mentioned pore phenomenon.
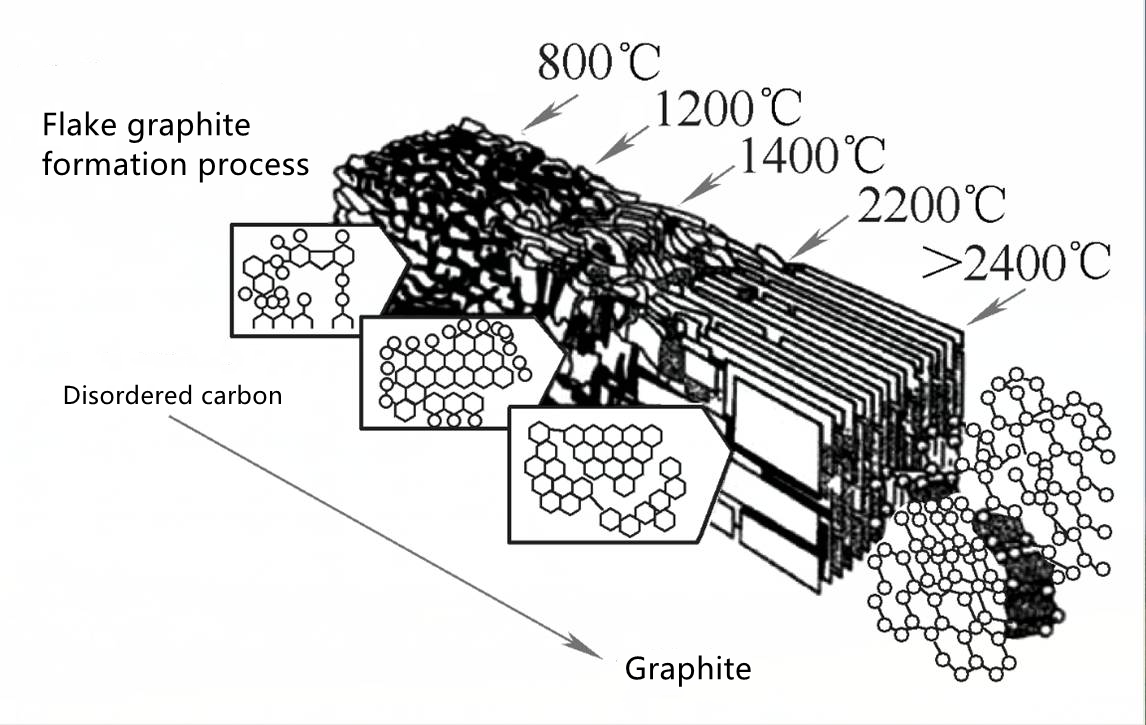
By the way, let’s talk about the understanding of the use of coal-based recarburizers: due to the low carbon content, high sulfur content and low ignition point of coal (anthracite at 700°C), the calcination temperature of coal-based recarburizers is around 800°C, and it is graphitized. The carbon atoms are disorderly arranged, and the carbon atoms are connected to each other, and it is not easy to get rid of the body. The recarburizer has dense macrostructure, smooth and hard texture, and contains many impurities, so its dissolution rate is slow and the absorption rate is low.
The carbon atoms undergo high temperature treatment. As the temperature increases, the arrangement of the carbon atoms changes from chaos and disorder to gradually orderly arrangement. Anthracite has a low ignition point and is difficult to calcinate at high temperature. It has not been calcined at high temperature, so it not only contains high impurities, but also retains the original coarse graphite. These coarse raw graphite (sheets) have a high melting point and strong stability. They cannot be completely eliminated during the smelting process with an intermediate frequency induction furnace. This is commonly referred to as "heredity". These coarse graphites that have not completely disappeared form the earliest graphite nuclei when the molten iron solidifies. They grow up together with other graphites, and their coarse graphites look like tadpoles and are called "C" graphites. Li Chuanshi pointed out in the article "Some Metallurgical Features of Gray Cast Iron Smelting with Induction Furnace" that the amount of nascent iron should not exceed 20%. He is worried that the coarse graphite in nascent iron will not be completely dissolved, which will result in "heredity." Adding nascent iron to the production ingredients is also worried about the "heritability". What's more, the carbon atoms in the coal have greater "heritability", which will affect the physical properties of the casting. Even if it is not reflected immediately, the workpiece is in the service process. , These coarse graphite flakes may become the source of cracks, affecting the fatigue strength of the castings and causing fractures. Due to the dense structure of coal-based recarburizers, the arrangement of carbon atoms is chaotic, and its absorption speed is slow, and it is easy to float on the surface of molten iron. The part that cannot be absorbed is not completely melted. Under the action of electromagnetic stirring, or hanging in the furnace On the wall, or wrapped in molten iron, the castings form slag inclusions, carbide holes, etc. During the solidification of molten iron, due to the expansion of graphite, pores and shrinkage cavities are easily formed where there is no molten recarburizer particles.
3. Factors affecting the absorption of recarburizers
(1) The quality of the
recarburizer itself. It is recommended to use calcined petroleum coke recarburizer or graphitized recarburizer, namely artificial graphite.
(2) Carbon content of molten iron Generally, the lower the carbon content of the molten iron, the higher the absorption rate of the recarburizer. When the wc of the molten iron is above 3.6%, it is difficult to recarburize.
(3) The silicon content of the molten iron The higher the silicon content in the molten iron, the more it affects the absorption of the recarburizer. This is because silicon has the effect of discharging carbon and reduces the solubility of carbon in the molten iron.
(4) Manganese content in molten iron The high manganese content in molten iron is beneficial to the absorption of recarburizers.
According to data, for every 0.1% increase in the initial carbon content, the recarburizer absorption rate decreases by 1% to 2%; for every 0.11% increase in silicon content, the recarburizer absorption rate decreases by 3% to 4%; every time the sulfur content increases by 0.1%, The recarburizer absorption rate is reduced by 1% to 2%; for every 0.1% increase in manganese content, the recarburizer absorption rate increases by 2% to 3%. It can be seen that when the initial carbon content in the molten iron is high, under a certain solubility limit, the absorption rate of the recarburizer is slow, the absorption amount is small, the burning loss is relatively large, and the absorption rate of the recarburizer is low. When the initial carbon content of the molten iron is low, the situation is reversed. In addition, the silicon and sulfur in the molten iron hinder the absorption of carbon and reduce the absorption rate of the
recarburizer. The manganese element contributes to the absorption of carbon and improves the absorption rate of the recarburizer. As far as the degree of influence is concerned, silicon is the largest, followed by manganese, and carbon and sulfur have less influence. Therefore, in the actual production process, manganese should be added first, then carbon, and finally silicon.
(5) The quality of charge and molten iron. Prevent serious oxidation of molten iron during smelting.
(6) Furnace operation. The recarburizer has not been absorbed, so the slag is constantly picked out, and the recarburizer and molten slag are picked out together.
(7) Adding time and method of adding the recarburizer should not be added to the bottom of the furnace first. Because of the high melting point of the recarburizer, it is slowly decomposed and absorbed by the surrounding of molten iron. Therefore, if it is directly added to the furnace bottom, it will not only prolong the recarburization. The decomposition time of the agent and the high temperature of the accumulation can also burn the bottom of the furnace into a sponge shape, and even burn the bottom of the furnace through. When there is a small amount of molten iron at the bottom of the furnace, the recarburizer should be added together with the scrap steel, and strive to add the calculated recarburizer when the furnace charge is added 3/5.
(8) Furnace temperature control Under normal production conditions, if the temperature of the molten iron is higher (about 1380°C), the carbon is more soluble in the molten iron, and the carbon increase efficiency is higher.
4. How to add recarburizer
We know that using an induction electric furnace to smelt the charge is that the induction coil generates a magnetic field through conduction, and an eddy current is generated in the charge. The eddy current generates heat to melt the charge.
The melting point of scrap steel is higher than that of cast iron, and the melting point of the recarburizer is higher. When the scrap is melted and after melting, the recarburizer is slowly dissolved and diffused by heating, so that the carbon in the recarburizer can be corroded and absorbed by the molten steel. The molten steel gradually turns into molten iron, which is often referred to as "synthetic cast iron".
In the process of smelting molten iron, the induction electric furnace has the characteristics of electromagnetic stirring and friction. The molten iron has a high overheating temperature, a long time of overheating, and friction stirring caused by induced current. The fine crystalline graphite in the molten iron, namely the spontaneous crystalline nucleus and the foreign crystalline core, will gradually dissolve in the molten iron and disappear, or float on the surface of the molten iron. It is bound with the slag-collecting agent and is picked out of the furnace, so that the material in the molten iron that can be used as the foreign nucleus of graphite during eutectic crystallization is greatly reduced.
Since the use of an intermediate frequency induction electric furnace not only has no carbon source, but also the carbon is burned. Therefore, in order to obtain a qualified carbon content, adding a recarburizer is an indispensable measure. In smelting, the correct operation method is also very important to the quality of the molten iron and the absorption rate of the recarburizer. The specific operation method is as follows: first add 30~50kg of new iron or recycled material to the bottom of the furnace → a small amount of scrap steel → (after molten iron) recarburizer + scrap steel → pig iron + recycled material.
Conclusion
To produce synthetic cast iron with scrap steel and recarburizer, when selecting recarburizer, the recarburizer should be selected according to the amount of scrap steel added. If the amount of scrap steel added is small, you can choose a recarburizer with an appropriately high nitrogen content; If the amount of addition is large, you can choose a recarburizer with a low nitrogen content. High-quality recarburizer not only has the effect of increasing carbon, but also has the effect of incubating molten iron. Since nitrogen is a gas after all, and it is not easy to detect and control, when buying recarburizers, it is better to try to buy recarburizers with low nitrogen content.

